14th July
1920
The British government issued a communique, expressing itsintentions to withdraw from the management of the Golden Temple and make alternative arrangements in concultation with Sikh members of the reformed Legislative Council. This was actually done to put off the matter by a year. However, the government’s procastination provoked the reformists to step up their campaign for immediate resignation of Arur Singh, the government’s appointed Sarbarh. Demoralised at government’s tactics, Arur SIngh appeared before the reformers at theiu Ja;\fIanwala Bagh Diwan with folded hands. He asked for forgiveness and announced his resignation. This convinced the authorities who now regarded it as a “decided victory for the party of reformers.”
1948
Deputy Prime Minister of India, Patel, eliminated the Sikh rulers and established the Patiala and East Punjab States Union, PEPSU.
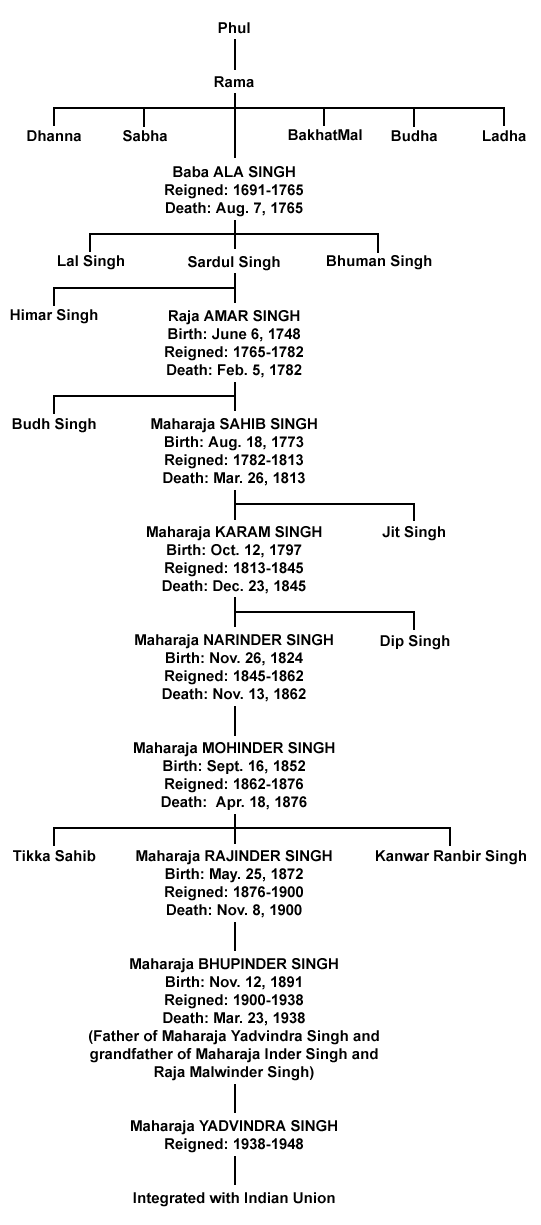
===> EAST PUNJAB STATES: Patiala, Nabha, Jind, Faridkot, and Malerkotla were the Sikh states in the East Punjab before the integration of Indian States in 1948. The first four were the Sikh states under the sovereignty of Maharaja Ranjit Singh and were brought under British protection by the 1809 treaty of Amritsar. Patiala, Nabha, and Jind, also known as Phulkian states, share a common ancestor Phul, who was descendent of Baryam. The Emperor, in 1526, had granted Baryam, the office of revenue collection for the waste country south-west of Delhi. Emperor Shah Jahan continued Phul in this office. From his eldest son descended the families of Nabha and Jind while from his second son the Patiala family. The Faridkot family, founded in the middle 16th century sprang from the same stock as the Phulkians chiefs.
The remaining two states were Kapurthala and Malerkotla. The Kapurthala rulers belonged to the Ahluwalia family. The real founder of this family was Raja Jessa Singh, a contemporary of Nadir Shah. The malerkotla rulers were Sherwani Afghans who traced their descent from Sheikh Sadruddin who had received 68 villages near Ludhiana in marriage gifts when he married the daughter of Sultan Bahlol Lodi.
The Sikh states geographically lay in three blocks. The main block comprising the territories of Patiala, Nabha, Jind, Malerkotla and Faridkot was in the centre of East Punjab and was fairly compact. Kapurthala State, composed of two enclaves in the Jullunder district, was in the north of East Punjab. The outlaying districts of Narnual, Dadri, and Badwal, which formed parts of Patiala, Jind, and Nabha States respectively, lay with the geographical orbit of the southern districts of East Punjab. There were also islands of Patiala State in what is now Himachal Pradesh.
At the time of India’s independence, there were divergent opinions as to the integration of the above states. On Feb. 11, 1948, Giani Kartar Singh, then President of Akali Dal, suggested the formation of the Union of Sikh States.He was opposed to the idea of merging those States with East Punjab, as it would further undermine the Sikh’s position who had suffered tremendously because of the partition of Punjab. On Feb. 22, there was a much advertised proposal to form a unit of 4 States of Est Punjab, but that proposal fizzled out because of disagreements among their rulers. The Nationalist Sikh opinion, though not vocal at that time, was in favor of a separate Union of all the Punjab States. Further, the government of India felt special responsibility to ensure that these States, particularly as they were border States, should be organized on proper and efficient lines. On May, 5, 1948, Patiala and Easy Punjab States Union, hereafter called PEPSU, was formed. The covenant was signed by the rulers of eight States, the Maharaja of Patiala signing also on behalf of the minor rulers of Kalsia.
On July 15, 1948, PEPSU was inaugurated. Sardar Patel called this occasion a landmark in the history of India’s progress. The area of PEPSU was to be 10,000 square miles, while its population was 34,24,060, and an annual budget of a little more than 5 crores. Sardar Patel administered the oath of to the Maharaja of Patiala as the first RajPramukh, who in turn administered the oath to Maharaja Kapurthala as teh UprajPramukh, swearing allegiance to the Centre and Indian Union, promising to do justice to all people in accordance with the laws and usages of the Country without fear, favor or ill-will. Due to the obvious differences between the three major parties at the time, no ministries could be announced. A care-taker ministry was formed with Sardar Gian Singh Raraewala as the head. The three major parties included Prajamandal (Congress party in the state was generally addressed by this name), Akali Dal, and Lok Sewak Sabha (patronized by Sardar Udham Singh Nagoke).
On Jan. 13, 1949, a broad based ministry was constituted to conduct the adminsitration of PEPSU. It comprised of Sardar Gian Singh Rarewala (as the head), Col. Raghbir Singh, Gianai Zail Singh, Chaudhri Nihal Singh Takshak, Pandit Ram Nath, Mr. Lachhman Dass Advocate, Sardar Ajit Singh of Rampura Phul, and Sardar Harcharan Singh Advocate of Bhatinda. Only 10 month later, this ministry was disolved and the government of India took over the administration of PEPSU.
On May 23, 1951, a 7-person ministry was sworn in. It consisted of Sarvshri Raghbir Singh (Col.), Brish Bhan, Giani Zail Singh, Nihal Singh Takshak, DEs Raj Gupta, Tirath Singh, and Sampuran Singh as cabinet ministers while Sardar Harchand Singh and Mr. Roshan Lal were the two deputy ministers.
On Jan, 7, 1952, PEPSU went to the polls for electing a 60-member state assembly with Congress winning 26 seats and Akali winning 19 seats. On March 1, 1952, Col. Raghbir Singh was unanimously elected as the Leader of the Congress Assembly Party. On March 19, the Congress Ministry was announced and administered the oath of office. Political activities in PEPSU centered around economic and social but certainly not on religious considerations. The problem of antagonistic relations between the landlords and tenants was so enormous that it almost defied a solution. Maharja Patiala’s father-in-law, Sardar Harchand Singh Jeji, played a vital role in PEPSU politics. He has always been associated with the Akali movement in the pricely States. After the settlement of disputes over the Gurudwaras, the Akalis from the states began to agitate against teh autocratic misuse of power by the maharajas, chiefly Bhupendra Singh of Patiala. Bhupendra Singh retaliated by having the leading agitator, Seva Singh Thikrivala, transfered from Lahore and interned in Patiala on false charges of theft. The Akalis took up the case of Thikrivala and let loose a campaign publicising Bhupendra Singh’s amorous escapades and the sadistic behavior of his police. Though Maharaja was able to win over a section of the Akalis, he could not silence the Punjabi and Urdu press.
In 1928, Akalis from the states joined with Hindu nationlists and founded the Praja Mandal (States People’s Association). The mandal was later affiliated to the All India States People’s Congress, which in turn was associated with the Indian National Congress. Sewa Singh Thikrivala was the moving spirit behind the Mandal. He was arrested several times and in 1935 succumbed to third degree methods practised on him by the Maharaja’s Jailers. As a result of the murder of Thikrivala, the anti-Maharaja, ant-British movement gained momemtum in all princely ststes of the Punjab.
As far as teh language problem, PEPSU was linguistically divided for educational purposes. The Hindi speaking region consisted of the districts of Mahendragarh and Kohistan (including Chhachrauli tehsil minus Dera Bassi) and the tehsils of Jind and Narwana. The rest of the State was declared to be Punjabi zone. In one zone, Hindi in Devnagri script; in the other Punjabi in Gurmukhi were made the media of instruction and in both the other language was made compulsory from the 4th primary class upwarsd. There was no provision for choice of the medium of instruction in Punjab.
-Ref. The Illustrated History of the Sikhs (1947-78), by Gur Rattan Pal Singh
==> PATIALA FAMILY traces its descent to Maharaja Gaj, founder of the town Gazni (now in Afghanistan) in the first quarter of the 16th century. His descendents, Maharawal Jaisal, founded the State of Jaisalmer and his grand son, Rao Hans Raj, is considered the ancestor of Patiala family. However, Tawarikh Guru Khalsa written by Giani Gian Singh, traces the Patiala family descent to Chaudhri Phul, a Sidhu Jat in “Malwa country” and the Chaudhri belonged to the 23rd generation of the family of Bhatti Rajputs. When Bhim Mal came to Punjab in 1237 he helped Shahabuddin Gauri, in his attack on Delhi and in lieu of that, he was given the area comprising of Hissar, Sirsa, etc. In 1251, he built a fort in Hissar town. After his death, his son Jawand Rao succeeded and had 21 sons. According to Giani Gian Singh, Chaudhri Phul, son of Chaudhri Rup Chand, belonged to the family tree belonging to the descendents of Jawand Rao. When Guru Har Rai Patshah visited Malwa in 1702 B.K., Chaudhri Kala, brother of Chaudhri Rup Chand, brought his two nephews, Phul and Sandali to the Guru. On instructions of their uncle, who was acting as their guardian, both Phul and Sandali started beating their bellies and when Guru Sahib asked the reason, Chaudhri Kala explained that his nephews wanted to sariate their hunger. At that time, Guru Sahib blessed and ordained that the Phul family would reign for a considerable period of time and that it would feed lakhs of people. Chaudhri Phul died in 1745 B.K. and was succeeded by his two sons, Talok Chand and Ram Chand, who were introduced to amrit by Guru Gobind Singh in 1761 and were subsequently named Talok Singh and Ram Singh. Because of their great services to Guru Sahib, the two brothers were blessed and the Guru ordained “My house is your house and I am much pleased with you”. Maharaj Ram Singh, who effectively controlled the areas surrounding Patiala, was murdered in 1771 B.K. (1741) at the hands of Chain Singh, Uggar Sain and Biru. He was succeeded by six sons, Baba Ala Singh proved to be the most dominating and promising. He was introduced to amrit by Nawab Kapur Singh.
The Patiala family attained prominence during Baba Ala Singh reign, who founded the State of Patiala by defeating the neighboring chieftains. Emperor Shah Jahan conferred the title “Raja” on Baba Ala Singh.
Unfortunately, the Patiala family often acted against interest of the Sikhs. They were often concerned with propagating their own family business interests firs and foremost. Among the damage they did to the Panth was the reinforcement of the Brahminincal tradition of Nirmalae Sikhs and in total disrespect to GurSikh women many Patialites kept countless Ranis, performed anti Sikhi parades, etc. When Gadarites were orgainzing in US and Baba Khadak Singh was pursuing Keys Morcha and Bhai Sahib Randhir Singh was organinsing Rakab Ganj protest, Patialites were busy bootlicking British reprentatives. They offered many naive young rural Sikhs for deployment in Greece, North Africa and Europe, who eventually sacrificed their lives for a war they had absolutely nothing to do with. The Sikhs continously failed to recognize Patialites and remained loyal to them, even during partition talks (when Patiala family’s daughter was to be wed with Dr. Ambedkar’s nephew and 100 million of Dalits who were going to embrace Sikhism were thrown out by a series of calculated malicious events).
For these reasons and many more, PATIALA FAMILY were never considered a part of the Khalsa Misls and remained as fringe elements to GurSikh society.
-Ref. The Illustrated History of the Sikhs (1947-78), by Gur Rattan Pal Singh.
1973
Bhai Sahib Harbhajan Singh Yogi met with the Archbishop of Canterbury to protest English laws which discriminate against Sikhs, particularly the law requiring motorcycle helmets.